This is a quick tutorial (mainly brain dump) on how I’m using Tilt do quickly iterate over my cluster-api-provider-openstack work.
Before you continue
- I won’t go into what CAPO, CAPI, Kind, ctlptl and Tilt are and how they work.
- I’ve just learnt about Tilt so this post will probably be updated from time to time.
- My environment always runs on latest stable Fedora, and latest dependencies (Kind, ctlptl, Tilt, etc).
- Check that your tools meet the latest requirements.
Podman
A couple of things I had to do regarding Podman:
- Enable the Podman socket:
systemctl --user enable --now podman.socket
And then in my zshrc I add:
export DOCKER_HOST=unix:///run/user/$(id -u)/podman/podman.sock
- Allow the local registry to be insecure, by editing
/etc/containers/registries.confand add:
[[registry]]
location = "localhost:5000"
insecure = true
Running out of inotify resources
My default Fedora had too low values for both max_user_watches and max_user_instances, so I tweaked it a bit:
sudo sysctl fs.inotify.max_user_watches=524288
sudo sysctl fs.inotify.max_user_instances=512
Deploy the Kind management cluster
ctlptl create registry ctlptl-registry --port=5000
ctlptl create cluster kind --registry=ctlptl-registry
I found ctlptl super useful as it handles the container registry, but you can also simply use Kind directly and deploy your own registry or e.g. use quay.io.
Create a Secret for clouds.yaml
For now I’m creating the secret “manually”, but I know Tilt can do it for us.
export CLUSTER_NAME=dev
export CAPO_DIRECTORY=~/go/src/github.com/kubernetes-sigs/cluster-api-provider-openstack
# replace `my_cloud` by the name of your cloud in clouds.yaml
source $CAPO_DIRECTORY/templates/env.rc ~/.config/openstack/clouds.yaml my_cloud
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: v1
data:
cacert: ${OPENSTACK_CLOUD_CACERT_B64}
clouds.yaml: ${OPENSTACK_CLOUD_YAML_B64}
kind: Secret
metadata:
labels:
clusterctl.cluster.x-k8s.io/move: "true"
name: ${CLUSTER_NAME}-cloud-config
EOF
Prepare CAPI
You need to create tilt-settings.yaml in the CAPI directory.
This is an example of how it could looks like:
build_engine: podman
kind_cluster_name: kind
provider_repos:
- ../cluster-api-provider-openstack
enable_providers:
- openstack
- kubeadm-bootstrap
- kubeadm-control-plane
debug:
openstack:
port: 31000
kustomize_substitutions:
CLUSTER_TOPOLOGY: "true"
CLUSTER_NAME: "dev"
OPENSTACK_SSH_KEY_NAME: "emilien"
OPENSTACK_BASTION_FLAVOR: "m1.large"
OPENSTACK_CONTROL_PLANE_MACHINE_FLAVOR: "m1.large"
OPENSTACK_NODE_MACHINE_FLAVOR: "m1.large"
OPENSTACK_FAILURE_DOMAIN: "nova"
OPENSTACK_IMAGE_NAME: "ubuntu-2204-kube-v1.28.5"
OPENSTACK_CLOUD: foch_openshift
OPENSTACK_DNS_NAMESERVERS: "1.1.1.1"
NAMESPACE: "default"
KUBERNETES_VERSION: "v1.28.5"
template_dirs:
openstack:
- ../cluster-api-provider-openstack/templates
Configure Virtual Studio Code
In the CAPO directory, create .vscode/launch.json:
{
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"name": "Connect to OpenStack provider",
"type": "go",
"request": "attach",
"mode": "remote",
"port": 31000,
"host": "127.0.0.1",
"showLog": true,
"trace": "log"
}
]
}
Make sure you have the Go extension installed and also you need to install Delve, a debugger for Go.
After that you can add breakpoints to your code and debug. Have a look at this guide for useful content.
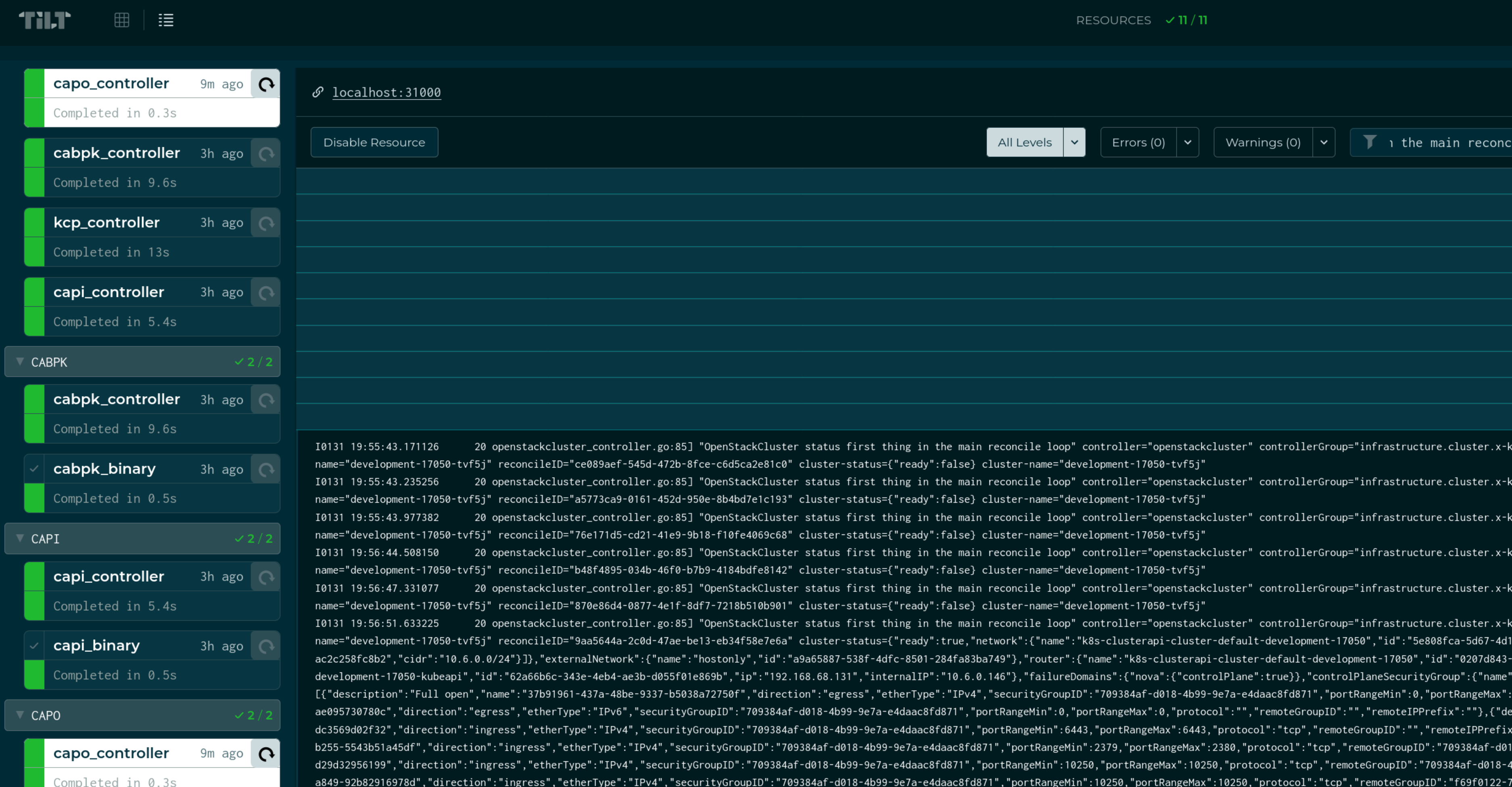
Run Tilt!
tilt up
Here is the URL to follow what Tilt will do, but basically it will do everything under the cover so when you change something in CAPO or CAPI or Tilt config, it’ll rebuild images and redeploy them in the management cluster.
To deploy a workload cluster, I do it from the UI:
- In
CAPO.clusterclasses, I apply thedev-testClusterClass. - in
CAPO.templates, I create adevelopmentcluster.
The cluster will now be deployed.